What is blood sugar
Blood sugar refers to the concentration of glucose in the blood and is one of the main energy sources required by the body to maintain normal physiological operations.
Glucose comes from the breakdown of carbohydrates in food, especially starches and sugars.

What is normal blood sugar level
There is a standard range for normal blood sugar levels, usually around 70 to 130 mg/dL on an empty stomach.
Two hours after a meal, blood sugar levels should remain within a range of less than 180 mg/dL.
This range helps maintain normal body functions and prevent metabolic diseases such as diabetes.
How to check blood sugar
A blood sugar check is done by measuring a small sample of blood drawn from a fingertip.
This can be done with a portable glucometer, which uses test strips to test the glucose concentration in the blood.
Depending on your doctor’s advice, a fasting blood glucose test or a postprandial blood glucose test may be needed.

The dangers of high blood sugar
High blood sugar can lead to a variety of health problems, including but not limited to:
Cardiovascular problems
High blood sugar can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Kidney problems
Long-term high blood sugar may lead to diabetic nephropathy, which affects kidney function.
Nervous system problems
High blood sugar may trigger neuropathy, leading to paresthesia and pain.
Vision problems
Diabetic retinopathy may cause vision loss or blindness.
What is diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease, mainly due to insufficient secretion of insulin or cell resistance to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar.
Diabetes is divided into type 1 and type 2, with type 1 usually caused by the immune system attacking cells in the pancreatic islets, while type 2 is related to lifestyle and genetics.
Diabetes symptoms
Symptoms of diabetes may appear gradually. Common symptoms include:
Drink more
Polyuria
Loss of weight
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Susceptible to infection
How to manage blood sugar
Blood sugar management includes the following aspects:
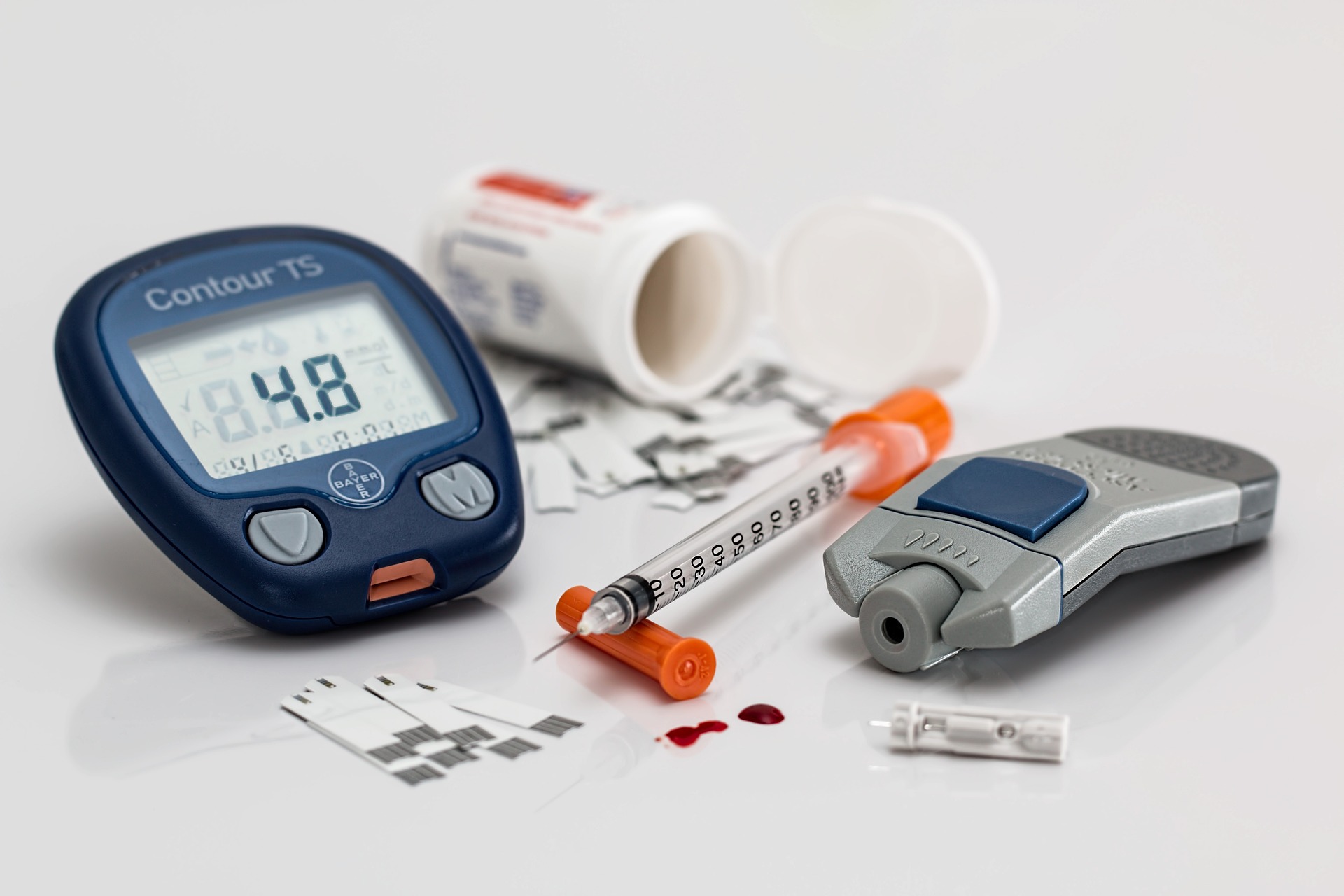
Medication
Use oral medications or insulin as recommended by your doctor to maintain blood sugar levels.

Healthy diet
Choose low GI foods, reasonably control carbohydrate intake, and focus on dietary fiber.

Moderate exercise
Regular aerobic exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity.
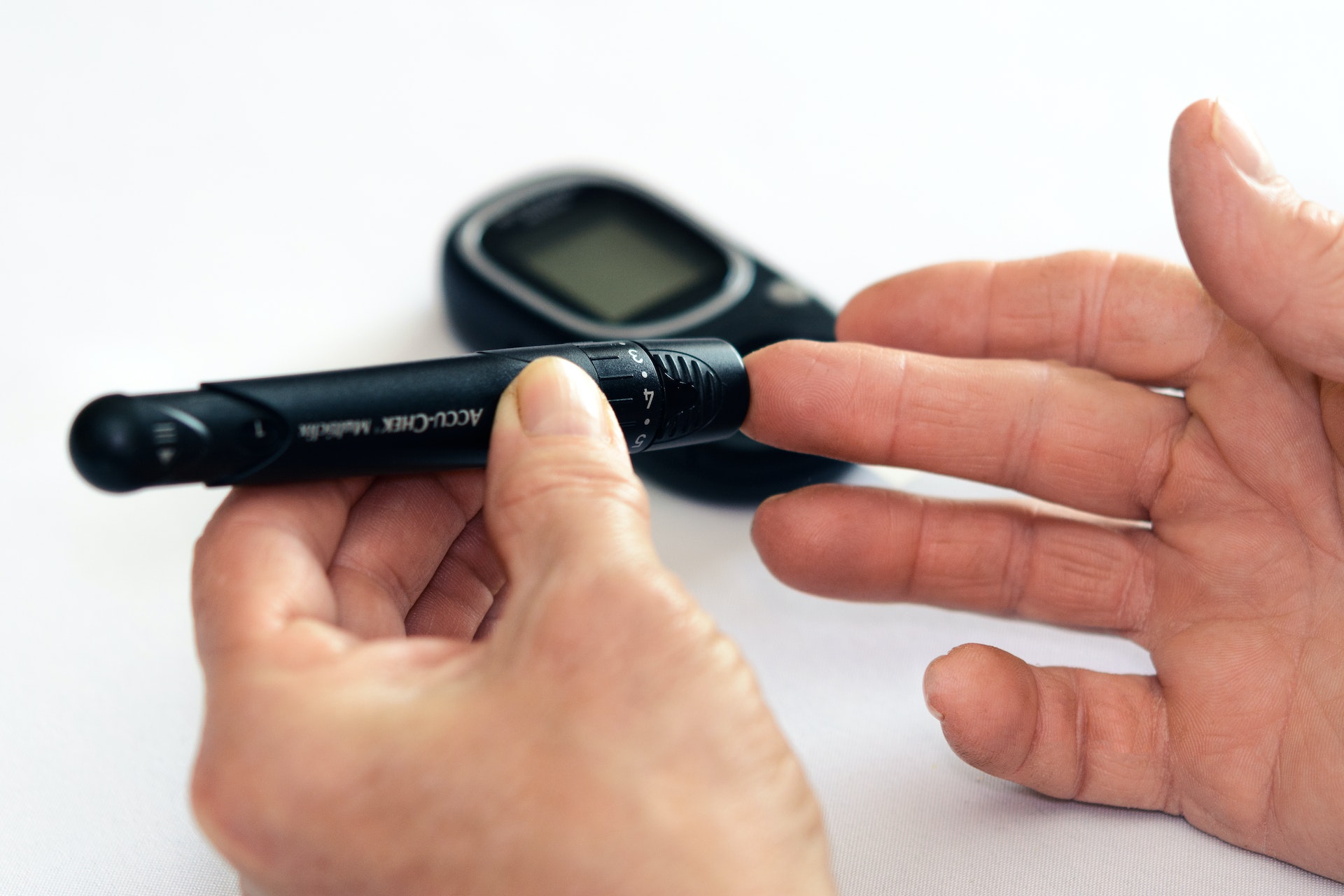
Regular monitoring
Make sure to check your blood sugar levels regularly and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.

Maintain a healthy weight
Controlling your weight is critical to blood sugar management.